Which Insulation Method is Best for Your Home: External Insulation, Internal Insulation, or Cavity Fill?
- MTS DNC ENERGY CONSULTANTS LIMITED

- Jan 14, 2024
- 4 min read
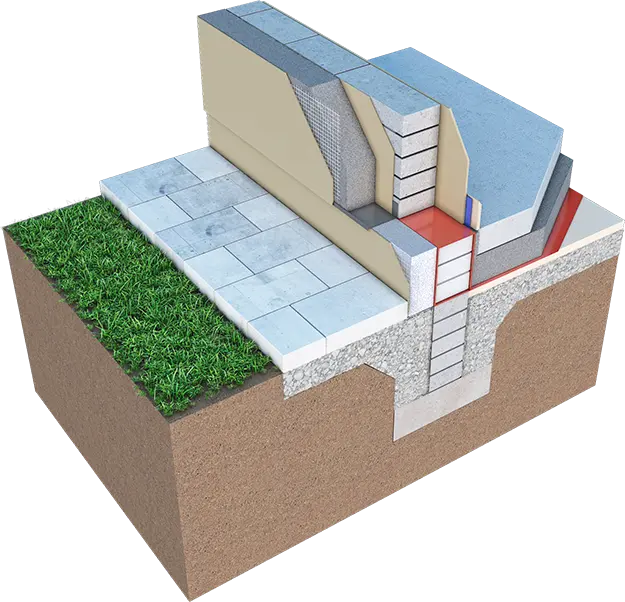
Based on the information gathered from various sources, here's a detailed comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of external and internal wall insulation:
External Wall Insulation Advantages:
Reduces Heating Costs: Insulation on external walls helps maintain a stable indoor temperature, leading to lower energy bills.
Enhances Thermal Comfort: It keeps the indoor climate more constant, regardless of outdoor weather conditions.
Minimizes External Noise: It acts as a sound barrier against street noise.
Protects Building Structure: Protects the building from harsh weather and wear, potentially extending its lifespan.
Improves Exterior Appearance: Can refresh the look of a building and possibly increase its value.
External Wall Insulation Disadvantages:
High Initial Cost: The investment for installation can be significant.
Potential for Moisture Issues: Incorrect installation may lead to dampness and mold.
Requires Skilled Installation: Professional expertise is needed for installation.
Alters Building Appearance: It can change the aesthetic of a building, which might not be desirable for historical buildings.
Susceptibility to Damage: External insulation can be easily damaged by weather or accidents.
Internal Wall Insulation Advantages:
Energy Efficiency: Reduces heat loss through walls, leading to energy savings and lower heating bills.
Appearance: Does not impact the external appearance of the house.
Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than external insulation.
Flexible Installation: This can be done room by room.
Internal Wall Insulation Disadvantages:
Space Consumption: This can reduce valuable floor space in smaller properties.
Condensation Issues: If not installed with a continuous vapor barrier, it can worsen existing damp or mold issues.
Thermal Bridging: This can cause thermal bridging around internal walls, windows, and doors, reducing thermal efficiency.
Disruptive Installation: This may require moving heavy items and cause disruptions during installation.
Advantages of Foam Cavity Wall Insulation:
Heat Loss Reduction: Foam insulation significantly minimizes heat escape from your home, leading to warmer interiors during winter and cooler in summer, thereby enhancing energy efficiency.
Lower Energy Bills: By retaining heat, foam insulation can lead to substantial savings on energy expenses.
Mold Prevention: Properly installed foam insulation can help prevent mold by restricting moisture passage through walls.
Improved Insulating Performance: Polyurethane foam, for instance, has a low lambda value, making it a highly effective insulator.
Environmental Benefits: Enhanced energy efficiency translates to reduced carbon emissions, contributing to a greener future.
Disadvantages of Foam Cavity Wall Insulation:
Installation Complexity and Cost: The installation process requires expertise and can be expensive, particularly when considering labor costs.
Potential Water Damage: Over time, polyurethane foam can shrink, potentially allowing water to seep into the cavity and cause damage.
Incompatibility with Some Structures: Not all buildings are suitable for cavity wall insulation; older buildings with solid walls may not have suitable cavities.
Ventilation Issues: Incorrect installation can affect indoor ventilation, which is crucial to prevent condensation and maintain good air quality.
Risk of Gaps and Reduced Insulation Over Time: The materials can shrink or pull away from the wall framing, reducing their insulative properties.
Conclusions
- Foam Cavity Wall: the foam cavity wall insulation brings notable advantages such as enhanced energy efficiency and effective mold prevention. However, it is essential to weigh these benefits against potential challenges like the complexity of installation, the associated costs, and risks such as water damage and compromised ventilation. Deciding on this insulation type should be grounded in a thorough understanding of the building's specific needs, compatibility with the insulation method, and a consideration of the long-term advantages versus initial investment.
- External Insulation: This is a preferable option when aiming to boost energy efficiency without impacting the internal living space. However, it tends to be more expensive and may alter the external aesthetics of the building.
- Internal Insulation: More appropriate for situations where maintaining the external appearance is crucial, such as with heritage buildings or in conservation areas. While more cost-effective, this method might reduce internal space and could lead to increased condensation issues if not correctly implemented.
Ultimately, the decision between different types of wall insulation hinges on a blend of factors, including financial constraints, structural limitations, and the specific requirements of the property. All insulation methods present substantial benefits in terms of energy conservation and overall comfort, yet each has its drawbacks. Careful evaluation of these aspects, in conjunction with the unique attributes of the building, is critical.
Disclaimer: The information provided here about insulation is for general informational purposes only and should not be seen as an exhaustive guide for installation or a detailed specification. Each home has unique characteristics, and insulation needs can vary significantly based on specific conditions, including local climate and building codes.
For precise and personalized advice, it's crucial to consult with a qualified insulation professional. They can conduct a comprehensive evaluation of your home and ensure that any insulation project is executed safely, effectively, and by all applicable regulations and standards. Moreover, adherence to local building codes and regulations is mandatory, and you should also consider the environmental impact and long-term sustainability of the insulation materials and methods selected.
#Insulation #BuildingCodes #EnergyEfficiency #ProfessionalConsultation #HomeInsulation #Sustainability #BER #SEAI #HEATPUMP #GRANT #TECHNICALASSESSMENT #BuildingEnergyRating #Energy #Assessor


